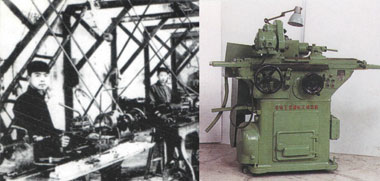
1 The origin of the Eighteen Arhats (1949-1957) When the founding of New China in 1949, there was no machine tool industry. Only some machine repair plants in Shanghai, Shenyang, Kunming and other places produced a small number of simple machine tools such as belt lathes, Bench drills, and head planers, such as the D-type 6 produced by Shanghai Mingjing Machinery Factory. Inch lathes, etc., the output of metal cutting machine tools was only 1,582 units, less than 10 varieties. Looking back, after the government took over the factory, it immediately invested a lot of money, purchased equipment, resumed and developed production, and began to change from the machine repair industry to the machine tool manufacturing industry, copying the machine tools of the United States and the United States and the former Soviet Union. In 1952, the number of metal cutting machine tools produced nationwide reached 30, with an annual output of 13,700 units. Figure 1 Machine tools produced in the early days of the founding The belt lathe and tool grinding machine produced in Shanghai in the early days of the founding of the People's Republic of China (the first modern machine tool in China) are shown in Figure 1. In September 1952, the Central Heavy Industry Department held a national machine tool conference, which made preliminary plans for the development direction of the machine tool products and the layout of the factory. In 1953, according to the recommendations of the Soviet experts, the division of labor and development direction of 18 machine tool factories nationwide was determined. Because of the high hopes of 18 machine tool factories shouldering the historical mission of China's industrialization, they were called "18 Arhats Factory". Among the 156 key construction projects of “One Fiveâ€, there are three machine tool industry: Shenyang First Machine Tool Plant, Wuhan Heavy Machine Tool Plant and Harbin Measuring and Cutting Tool Factory. In 1955, Shenyang First Machine Tool Plant completed the reconstruction of the former Soviet Red Promised Machine Tool Plant, and established 7 production lines with an annual output of 2,200 ordinary lathes of 2,200, which is a world-class machine tool factory at that time. In 1956, the Ministry of Machinery Industry began to carry out technical transformations in batches and batches of 27 machine tool factories, tool factories and accessory factories, including Kunming Machine Tool Plant, and initially established China's modern machine tool industry; among them, the size and main scale of the 18 Luohan machine tool factory at that time. The products are shown in Table 1. Table 1 Overview of the 18th Arhat Machine Tool Plant in 1957 It can be seen from Table 1 that by the end of the “First Five-Year Plan†period, the varieties produced by China's machine tool industry have been quite complete, and the scale (personnel) has reached a considerable extent, and the proportion of technicians has reached 8%.