Before the emergence of wheat to winter, the temperature is suitable, and the weeds also ushered in the peak of emergence. At this time, the use of herbicides for chemical control is the best. However, there are too many varieties of wheat herbicides, and many friends will not know how to choose. No problem, after reading this article, you will not only choose to use it, but also tell others, be an expert! First, the type of weeds in the wheat field There are about 30 main weeds in winter wheat. The main weeds in the south of the Huaihe River are grass weeds, such as Mai Niang, Japanese Mai Niang, Baked Wheat, Bluegrass, Hard Grass, Bole Grass, and Miscanthus. Broad-leaved weeds mainly include swine fever, bovine broth, mother-in-law, broken rice, sorrel, stalk, big nest and so on. There are many weed species and complex communities in the wheat fields of the Huanghuai River Basin. The weed species in the rice-wheat crop wheat field are similar to those in the south. Seeing Mai Niang and Japan watching the Mai Niang, some wheat fields such as hard grass, head grass, wild oats, miscanthus and buckwheat are seriously harmful. Huanghuaihai is an early winter wheat weed, mainly consisting of pork chop, wild rapeseed, sown wormwood, big nest, maijiagong, leeks, lacquer, mother-in-law, snail, thorn, and rice.藜, Xiaoyan, 匾 和 and Baoga grass are the main ones. Winter wheat in the Loess Plateau of Shanxi and Shaanxi provinces is heavier with thorny vegetables, alfalfa, crane wind, lone vegetables and ion grass. There are more than 20 kinds of weeds that are seriously endangered in spring wheat fields, mainly including alfalfa, coiled stalks, mold leaf stalks, camphor, duck sedge, wolf grass, sorghum, sky blue scorpion, wild oats, wild buckwheat, green foxtail, alfalfa Grass, ridiculous, etc. The Qinghai-Tibet and Chuanyun-Gui are high-altitude spring wheat areas. The main weeds include wild oats, bristle, snail, scorpion, scented scent, scorpion, stalk, wild buckwheat, big thorn, and valerian. In the Xin, Gan, Ning and Mengchun wheat areas, the main weeds include wild oats, field spines, reeds, wild mustard, chicory, sorghum, alfalfa, and big thorns. Second, the use of herbicides for weeds Note: “=†means that the control effect is similar, and “>†means that the control effect has a high order. Control agent for grass weeds (1) Look at Mai Niang. The efficacy of oxazocilin, acetyl oxalic acid, methyl disulfuron, flucarbazone, isoproturon, oxazolin, acesulfame, etc., are more than 90%. (2) Resistance to look at Mai Niang. There are isoproturon, macromolecule (oxazolyl oxalic acid), acesulfame and the like. (3) Japan looks at Mai Niang. Isoproturon = oxazolinol = acesulfame = acetyl oxalic acid = oxazolidine > methyl disulfuron > fluorokesulfuron. (4) Wild oats. Acetyl oxalic acid> benzoxazole and oxazolidine>isoproturon>oxazolyl grass>flurazolesulfonate>oxazolyl grass. (5) Hard grass. Acetyl oxalic acid> benzoxazole and oxacillin> isopropyl sulfonate > oxazolin grass > methyl disulfuron > fluorokesulfuron. (6) Valerian. Acetyl oxalic acid> benzoxazole and oxalic acid>isoproterenol>oxazolyl grass> fluzilsulfonate>methyldisulfuron. (7) The head grass. Vinyl oxalate, methyl disulfuron, and oxazolin. (8) Festival wheat. Methyl disulfuron. (9) Beech. Isosulfamide > flufensulfuron > methyl disulfuron. (10) Bluegrass. Methyl disulfuron > flufensulfuron > acesulfame. (11) Candle grass. Acetyl oxalic acid = oxazolinol = acesulfame = isoproturon > oxazolamide > methyl disulfuron. (12) Alkali. Methyl disulfuron. (13) Ryegrass. Methyl disulfuron, oxazolin, acetyl oxalic acid, metsulfuron-methyl, acesulfame. 2. Control agent for broadleaf weeds (1) Traditional. Methyl disulfuron, kusima, Maixi, Mishida, oxasulfuron, dextromethorphan, dimethyltetrachloro, chlorofluoxyacetic acid, acesulfame. (2) Niu Fanyu. Methyl disulfuron, isoproturon, acesulfame, oxasulfuron, dextromethorphan, dicamba, flupiroxyacetic acid. (3) Roll ears. Fluroxypyroxyacetic acid, maixi, maisida, acesulfame, oxadiazon. (4) Miva cans. Isosulfuron, Maixi, Mishida, fluoxetine. (5) Big nest vegetables.阔世玛, fluoxetine, methyl disulfuron, maixi, 麦施达, oxasulfuron, chlorhexidine, acesulfame, dicamba, metformin, clopyralid . (6) Sowing the wormwood. Methyl disulfuron, vassal, isoproturon, oxadiazon, mexi, maisida, acesulfame, chlorhexidine, 24-D, thifensulfuron, sulfimsulfuron. (7) Resistance to the sage. Mishida, oxazolone. (8) Amaranth. Fluazosulfuron, Mai Shi Da, Mai Xi, oxasulfuron, oxazolone, chlorhexidine, metformin, acesulfame, 24-D, kusima, dicamba, sulfonate Amine, flupiroxyacetic acid. (9) Stop blue vegetables. Zoxacondone, oxasulfuron. (10) Broken rice bran. Kuoshima, Maixi, oxasulfuron, oxadiazon. (11) Buddha. Fluroxypyroxyacetic acid, plus a large amount of acesulfame. (12) Ze paint. Fluroxypyroxyacetic acid, Mexi (inhibition), Mishida, diflufenacil (inhibition), oxadiazon, 24-D. (13) Mai Jiagong. Isoproturon, Maixi, Mishida, diflufenacil, oxadiazon. (14) Mother-in-law. Kusma, acesulfame, and oxadiazon are widely available. (15) Swine fever. Diflufenacil > flupiroxine > > oxadiazepine > dicamba. (16) Hey. Isoproturon, tribenuron, oxazolone, 24-D, thifensulfuron, sulfimsulfuron, dicamba, flufenoxyacetic acid, acesulfame, and flufensulfuron. (17) Rolling stems. Fluroxypyroxyacetic acid, flufensulfuron, oxazinone, clopyral acid. (18) Tian Xuanhua. Zoxaconone, fluproppiroxyacetic acid, chlorhexidine, 24-D, dicamba. (19) Bowling flowers. Zoxacondone, fluproppiroxyacetic acid. (20) thorny vegetables. Mishida, oxazolone, 24-D, clopyralid, dicamba. (21) Rice leeks. Isosulfuron, oxazinone, clopyralid, valer. (22) Wild old man. Fluroxypyroxyacetic acid, dimethyltetrachloro, oxadiazon, pyripramine, diflufenacil, acesulfame. (23) Scribbled. Fluroxypyroxyacetic acid. Third, the advantages and disadvantages of various herbicides Wheat field grass weed control agent (1) methyl disulfuron Advantages: Suitable for use in soft and semi-hard winter wheat varieties. The drug has a short residual effect in the soil and does not affect the growth of the lower crop. Disadvantages: high cost and strict medication technology. If the application rate per acre is more than 40ml or the application is too late, the yellowing of the wheat will be caused. (2) acesulfame Advantages: The confrontational and mutated look of Mai Niang is good and the promotion potential is great. It is more comprehensive to control grass weeds, including buckwheat, wild oats, hard grass, etc. It has good effects on hard-to-protect broadleaf grasses, such as wild cockroaches, mother-in-law, big nest vegetables, and resistant cattle. No effect on the helium, low temperature requirements. Disadvantages: Wheat should not be applied after it has been lifted. Safety is different among different wheat varieties; wheat seedlings are weak and the risk of phytotoxicity is high; unfavorable climatic factors will increase the risk of phytotoxicity. There is cross-resistance between Shima and Shima, and structural differences can delay the development of resistance; some Shima and Koshi have been widely used for many years, and the risk of priority resistance is high. (3) acetylacetoate Advantages: Excellent resistance even in many complicated environments such as low temperature, rainy, and dry. Disadvantages: The death from acetylene ester to weeds is relatively slow, usually takes 1 to 3 weeks. The drug should be used as early as possible, and the resistance of the weeds after tillering is enhanced, and the control effect is poor. (4) oxazolamide Advantages: It can effectively prevent a variety of grass weeds such as wild oats in the wheat field, see Mai Niang, Japanese maiden, hard grass, ryegrass, yarrow, etc. It has poor control effect on buckwheat and is ineffective against broadleaf weeds. Disadvantages: The drug should be used as early as possible, the resistance of the weeds after tillering is enhanced, and the control effect is poor, so the spring anti-drug should be appropriately increased after the year. When the drug is exposed to low temperatures, the wheat leaves will be slightly yellowed and will eventually return to normal with their growth. (5) flucarbazone Advantages: It can control malignant grass weeds such as bluegrass, ryegrass, brome, wild oats, and some broad-leaved weeds such as leeks, wild peas, and blue cabbage. In the field of mixed grasses and weeds such as leeks and bluegrass, this medicine can be preferred. The drug can be administered from the 2nd leaf stage of wheat to before the jointing. Disadvantages: The drug has a poor control effect on the wheat, and the field with the dominant wheat as the dominant population should be applied before the weed 1 leaf 1 heart period. When the grass age is large, other grass control weeds should be considered. Herbicides. (6) Wild wheat Advantages: It is used to control grassy weeds such as wild oats, maiden, bluegrass and poisonous wheat. Disadvantages: Wild wheat has a volatility. After application, the disc must be placed on the ground with a disc harrow or a dent, and the medicament is mixed into a soil layer 10 cm deep, and then the wheat is planted and the depth is 3 to 5 cm. 2. Broadleaf weed control in wheat field (1) Bensulfuron Advantages: safety, wide spectrum of herbicides, long application period, low environmental impact and low cost. In the weed community, the weeds with the advantage of wheat straw, leeks, alfalfa and bowls are better. Disadvantages: Peanuts and peppers have a safe interval of 120 days. In recent years, the use of control effects has decreased, and lacquer, leeks, and sage are produced to varying degrees of resistance. Weeds responded slowly, and all died 4 weeks after the drug. Prevent the liquid from drifting onto sensitive broadleaf crops during spraying. (2) Bensulfuron-methyl Advantages: safety, wide spectrum of herbicides, long application period. It can prevent most broadleaf weeds and has better control effect on piglets. Disadvantages: The effect below 10 °C is poor, the speed of dead grass is slow, and the safety interval of peanuts and peppers is 60 days. The soil must be moist when used in wheat fields, and if the soil is dry, the soil is less effective. (3) Thiosulfuron Advantages: safety, wide spectrum of herbicides, long application period, weeds react slowly to the drug, use drugs at low temperature, and all weeds can die more than 4 weeks after drug administration. Disadvantages: The effect below 10 °C is poor, the speed of dead grass is slow, and the safety interval of peanuts and peppers is 60 days. It is not effective for weeds such as Tianxuanhua and thorny vegetables. (4) 2 A 4 chlorine Advantages: low cost, fast speed, no residue, and safety for crops after harvest. It has a good effect on cruciferous weeds such as sage, leeks, lacquer, and glutinous glutinous rice, but it has effects on Maijiagong, Po Po Na, Pork, Miwa, garnish, and big nest. Basically invalid. Disadvantages: short pot life, excessive, low temperature on wheat has phytotoxicity. When the temperature is lower than 18 °C, the effect is obviously deteriorated, and the effect on unearthed weeds is not good. The volatility and speed of action are lower and slower than 2,4-D, and dimethyltetrachloride is sensitive to the seedling stage of gramineous plants. (5) dicamba Advantages: fast speed, no residue, safe for rear crops, good control effect on piglets. Disadvantages: short pot life, excessive, low temperature on wheat has phytotoxicity. Sensitive to dicotyledonous crops, avoid spraying the liquid to the dicot crop field when applying. At the same time, it is strictly prohibited to contact crop seeds. (6) Isoproturon Advantages: The speed is faster, and the seedlings can be used after the seedlings, and the monocotyledonous weeds such as Mai Niang, hard grass and wild oats are better, and the control effect on the dicotyledon weeds is also better. Governance resistance is better for buying mother and hard grass. It is also effective against bluegrass. Disadvantages: Due to environmental impact, poor safety, high risk of phytotoxicity, especially low temperature (average daily temperature below 4 °C) and smear; stop application 1 week before cold current; weak wheat, will also aggravate phytotoxicity. In addition to the poor effect of broadleaf weeds, the amount used in early spring is more than double that of the previous year. (7) flufluoxyacetic acid Advantages: wide spectrum of killing grass, safety, and rapid drug effect. It has good control effect on swine fever, sorghum, big nest and lacquer. Disadvantages: The short-lived period is affected by the low temperature in winter. When the medicine is used, it must be controlled at a temperature higher than 10 °C. Should be used as much as possible in the weed seedlings, weed plants have a greater impact on weeding effect. (8) diflufenacil Advantages: Stable at low temperatures, even at 2 ° C to ensure stable efficacy, which is unmatched by other herbicides. It can prevent most broad-leaved weeds in wheat fields, including the difficult to prevent weeds such as swine fever, Maijiagong, Fanzhi, Amaranth, and Compositae, and has a very good inhibitory effect on the most difficult-to-remove paint in wheat fields. Disadvantages: Dead grass is slow. Low temperature does not affect the final weeding effect, but it affects the speed of effectiveness. (9) oxasulfuron Advantages: The speed is general and has special effects on piglets. It also has a certain inhibitory effect on young grass weeds. Disadvantages: high price, narrow grass killing spectrum. Rape, beet and cotton are sensitive to the drug. Stem and leaf treatment should be selected in sunny days, when the temperature and humidity are suitable, the herbicidal effect will be reduced under drought and cold conditions. (10) acesulfame Advantages: safe, fast, and wide-ranging. Disadvantages: Weeds are prone to recurrence, and only under the light conditions can the full effect be achieved. After treatment, the wheat leaves had different yellow burn spots of different degrees, and the spots gradually disappeared after 7 days. (11) Pyriprene Advantages: safe, fast, and wide-ranging. The amount of acre is very low, and a good effect can be obtained with an effective ingredient of 0.4 g to 0.6 g. It is especially good for piglets, bowls of flowers, gray vegetables, simmering and cumbersome. Disadvantages: high price, weeds are easy to relapse, wheat has drug spots. It has a contact-killing effect on weeds only, and there is no soil sealing effect. In the period of drug use, it should be carried out as much as possible after the emergence of most of the weeds in the field. (12) oxadiazon Advantages: wide grass killing spectrum, especially can prevent a variety of malignant broad grass: lacquer, resistant seed wormwood, leeks, mother-in-law, pig scorpion, wild scorpion, etc. (for big nest vegetables, rice leeks, sorghum The effect is general, the effect on the embellishment is poor); the killing speed is fast. It has good activity against weeds and the like which are resistant to sulfonylurea herbicides. Disadvantages: high price, weeds are easy to relapse, wheat has drug spots. It has a contact-killing effect on weeds only, and there is no soil sealing effect. In the period of drug use, it should be carried out as much as possible after the emergence of most of the weeds in the field. Surfactants such as synergists and washing powders should not be added. It should not be mixed with oxazole and grass, otherwise it is prone to phytotoxicity. (13) sulfensulfuron Advantages: The drug has a short residual effect in the soil and generally does not affect the growth of the lower crop. It is used to control the broad-leaved weeds such as pork mites, sown wormwood, leeks, lone stalks, alfalfa, sorrel leaves, stalks, snails, and chicory. Disadvantages: The drug should be used as early as possible, and the amount of the drug should be appropriately increased when the weed leaves are old or the weather is dry and the conditions are not poured. After the weed leaves absorb the agent, they stop growing, the leaves are chlorotic, and then die. Fourth, the main wheat field herbicide formula on the market 1. The main single agent on the market (1) 69 g / L of thiazol and grass water emulsion. It is used to control grass weeds in the early stage of winter wheat field. It has better effect on looking at Mai Niang, wild oats, hard grass and alfalfa, and has lower cost. It is not effective for dicotyledon weeds and grasses. The drug is greatly affected by the low temperature in winter, and the temperature must be controlled above 10 °C. (2) 3% methyl disulfuron oil suspension. It can prevent a variety of grass weeds such as wild oats, brome, bluegrass, and ryegrass. It is a good agent for controlling difficult grass weeds. For the 5th leaf stage of wheat to the end of tillering stage, 20~30ml/mu, the application rate per acre is more than 40ml or the application is too late will cause wheat yellowing phytotoxicity. (3) 70% fluzolsulfonate water dispersible granules. It can effectively prevent the grass weeds in the wheat field - buckwheat, and has excellent control effect. In winter, the use of medicine in the greening period of wheat can also control the damage of buckwheat, but the control effect is not as good as that before winter. For the buckwheat, the maiden, the Japanese maiden, the effect is good, and the effect on hard grass, wild oats, candle grass, and martial arts is poor. (4) 75% bensulfuron dry suspension. Mainly control broadleaf weeds in wheat fields. In the weed community, the weeds with the advantage of wheat straw, leeks, alfalfa and bowls are better. It has good control effect on some broadleaf weeds. However, the current problem of weed resistance is outstanding. (5) 480 g / liter of wheat grass water-wet agent. It has fast speed and no residue. It is safe for crops after harvest, but the application period is short. Excessive and low temperature have phytotoxicity to wheat. (6) 15% acetyl oxalic acid wettable powder. It is mainly used to control wild oats, maiden, oats, ryegrass, common bluegrass, and foxtail. It has a slightly poor control effect on hard grass, and is ineffective against brome, bluegrass, and knotted wheat. In the case of wheat seedlings suffering from drought, waterlogged, frozen and growing, it is prone to phytotoxicity. (7) 20% flufenoxyacetic acid emulsifiable concentrate. It has strong systemic absorption and high activity. It is more difficult to control weeds, such as swine fever and lacquer, and it is safe for wheat. However, the speed of dead grass is affected by temperature and the cost is also high. (8) 40% oxazolone dry suspension. The recommended dosage per acre is 2 to 4 grams. The speed of killing grass is fast, and the effect on the burning of lacquer is obvious. It can prevent a variety of weeds such as lacquer, wild geranium, mecca, piglet, mother-in-law, broken rice bran, rice bran, and ear, but it is more effective against big nests, sorghum, and cattle. difference. 2. The main compound preparations on the market (1) Bensulfuron + oxazolone (Quomachlor). This formula kills grass quickly and has better control effect on piglets, but the cost is higher. (2) oxazolone (fast chlorpheniramine) + 2 methyl 4-chloro. This formula is very fast, especially for swine fever. (3) Methyl disulfuron + methyl iodsulfuron. This formula has good control effect on almost all grass weeds. Among them, methyl iodsulfuron has good control effect on broad-leaved weeds and mother chrysanthemum, and also has wild oat and bluegrass. Better control. (4) Acetazosulfuron + methyl iodsulfuron. High-efficiency, broad-spectrum and selective herbicides for most common malignant broad-leaved weeds such as swine fever, big nest vegetables, wild vulgaris, mother-in-law, sage, and sorghum. (5) Zoloxacin + acetyl oxalic acid. It has quick effect on broad-leaved weeds and can control grass weeds that are resistant to thrips; it has good effect on oats and ryegrass; it is sensitive and active to Mt. The effect on older grass is better, and no obvious phytotoxicity has been found. (6) Benzosulfuron + acesulfame has a number of "1+1" forms of wheat field herbicides using this formulation. Compared with the use of bensulfuron alone, this formula can increase the control effect on difficult to control weeds such as swine fever. (7) Bensulfuron + 2,4-D This formula is very effective against piglets and the price is also cheaper. However, there is one biggest drawback: 2.4-D is easy to drift pollution, and the sprayer must be used exclusively, and can only be used in cereal crops such as wheat, corn, rice, etc., and is susceptible to phytotoxicity on broad-leaved crops. (8) flufluoxyacetic acid + bensulfuron-methyl This formula has three major characteristics: First, the effect is good, and it is effective for all broad-leaved weeds, especially for malignant weed lacquer and piglet; Second, weeding does not rebound at all; third is quick effect, basically three days effective, one week dead grass. (9) Bensulfuron-methyl + bensulfuron-methyl This formula has good acceptability in southern North China, and the speed of dead grass is 20~30 days. It has good control effect on common wheat field weeds, but it is not effective against big grass and resistant grass. (10) Bensulfuron + acetyl oxalic acid has the function of "we broad and double division", which saves time and effort. The product market is mainly located in the area of ​​Susie Rice and Wheat Rotation. (11) Diflufenacil + 24-D isooctyl ester. It can prevent most broad-leaved weeds such as piglets, Maijiagong, Fanzhi, broken rice bran, leeks and wild rapeseed, and has a good inhibitory effect on lacquer. It is stable at low temperatures and stable even at 2 °C. (12) Diflufenacil + Zolziramide. It can prevent broad-leaved weeds such as sage, amaranth, and sorghum, and weeds are applied at the 3~6 leaf stage after emergence of wheat. (13) Diflufenazone + oxazolone This formula can control grass weeds and broadleaf weeds at one time, and control resistance to sage, resistant pig mites, leeks, sorghum, lacquer, etc. Broad-leaved weeds in a wheat field. The herbicide spectrum is wide, the speed is fast, the weeding does not recur completely, and the climate impact is small. (14) oxazolone + bensulfuron + sodium dimethyl tetrachloride mixed to solve resistant weeds (such as resistant sage, resistant leeks) and strengthened the lacquer and pig 殃殃The control effect effectively improves the control effect on the sorghum and the big nest vegetables, but the application conditions are restricted, and must be used before the four-leaf stage of wheat to before jointing. (15) Bensulfuron + bensulfuron-methyl + acesulfame-containing mid-range herbicide, good quality. In addition to the poor effect on the lacquer, all the broad-leaved herbs in the wheat field are cleared to the grass, which is quick and does not rebound, and the weeding is thorough. (16) Diflufenacil + Zolziramide + Isoproturon can prevent broad-leaved weeds such as swine fever, sown wormwood, leeks, and sorghum, and grass weeds such as maiden and hard grass. It is better to apply the herb in the 2~4 leaf stage before winter. (17) diflufenazone + oxazolamide + oxazolamide can prevent broad-leaved weeds such as swine fever, sown wormwood, leeks, and sorghum, and grass weeds such as maiden and wild oats . Weeds are applied at 3~6 leaf stage. When the soil moisture is high, the dosage is reduced. 5. What is the best time for medication? 1. The best period of control of wheat weeds during the best period of application is the wheat seedling stage and the greening stage. Weeds are controlled in the wheat seedling stage. At this time, the weeds are relatively young, and the resistance to the drugs is relatively small. It is easier to control and the dosage is not large. The greening period is also a favorable period for controlling weeds. However, at this time, the weeds are older and the drug resistance is stronger. In the prevention and treatment, it is necessary to increase the dosage. In this case, the cost of medicines will be increased invisibly, and wheat is easily caused. The phytotoxicity of the crops and adjacent crops. 2. Grasp the favorable timing of medication. In addition, the wheat weeding should pay attention to the weather temperature and humidity. When using the medicine, the average temperature should be higher than 6 °C, and it is best from 10:00 am to 3:00 pm. If the soil is relatively dry, it should be noted. Increase the amount of water, if there is water, it will affect the efficacy of wheat herbicides. Therefore, when applying wheat herbicides, it is necessary to seize the opportunity, consider in many ways, and timely use the medicine to lay the foundation for high yield of wheat. More pesticide knowledge , please pay attention to China Pesticide Network
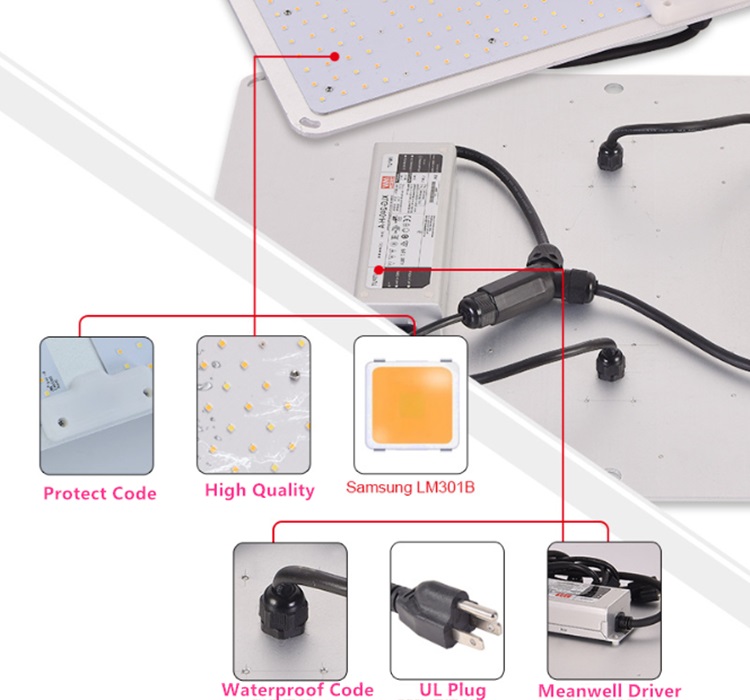
Grow Light Led 600w, with 6pcs boards, each board 350pcs led, high power grow light works well for large area, such as grow tent, hydroponic, We have samsung LM301B/LM301H led, also Samsung 5730 led, meanwell driver/normal driver available here.
Application:
Quantum board LED grow lights is a great ideal for all kinds of indoor garden plants: lettuce, orchid, organic herbs, pepper, strawberries, succulent, hydroponic, medical plants.
Hydroponic Grow Lights,Full Spectrum Led Lights,Succulent Grow Light,Sun Lamp For Plants Shenzhen Wenyi Lighting Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.szwygrow.com.jpg)