Gate Valves are called "full-flow" valves; there's a direct unobstructed path for flow right through the middle of the valve. A wedge-shaped brass gate is lowered into a machined slot to close the valve. They should either be completely open or completely closed. Water flowing through a partially open gate valve wears away the metal and causes the valve to fail over time. Brass Gate Valve, Flanged Gate Valve, High Pressure Gate Valves, Water Gate Valves ZHEJIANG KINGSIR VALVE CO., LTD. , https://www.cn-kingsir.com




As a high-end CNC machining equipment, the 5-axis linkage blade machining center has the characteristics of high automation, high processing efficiency and high machining precision. It is mainly used for the processing and manufacturing of core components of steam turbines, aero engines, blowers, axial compressors and other equipment. . The efficiency of equipment such as steam turbines depends to a large extent on the design and manufacturing level of the blade profile.
With the rapid development of power, energy, aerospace and defense industries, the production capacity of steam turbines and gas turbine manufacturers will further expand, and the demand for high-end blade processing equipment will also increase significantly. The demand for high-end five-axis linkage blade milling equipment will also increase. There has been a substantial increase. It is an urgent requirement for the entire blade industry to develop a domestic five-axis linkage blade machining center with excellent quality, reduce the cost of blade processing machine tools, and meet the needs of the blade industry.
1. Five-axis linkage blade machining center
The five-axis linkage blade machining center is the key equipment for processing turbine blades and navigation blades. At present, the domestic aerospace engine plant, steam turbine plant and blade professional production plant mostly use the imported five-axis linkage CNC blade machining center, and the blade finishing market is completely monopolized by foreign machine tool manufacturers. Due to the special nature of the five-axis linkage blade machining center, the price of the foreign five-axis linkage CNC blade machining center is prohibitively expensive, and the maintenance cost of the machine tool is difficult for the user to bear. In the face of the international situation, there is even more possibility of being blocked. Therefore, it is urgent to develop a new generation of high-quality domestic five-axis linkage blade CNC machining center that can compete with foreign high-end products, in order to break the monopoly pattern of this type of products abroad, and gradually realize the localization of domestic blade processing equipment and reduce blade processing. The equipment input cost of the enterprise.
As shown in Figures 1 to 4, the manufacturers of five-axis linkage blade processing centers abroad are well-known: Starrag Heckert, Liechti, and Italian Ferrari ( CBFerrari) and Hamuel of Germany. The common feature of the foreign five-axis linkage blade machining center is that the torque motor is commonly used for the A and B axes. The tool spindle adopts the electric spindle structure. The maximum speed of the tool is between 12 000 and 20 000 r/min, or even higher. The tool interface is HSK- A63 is mostly; the speed of each linear axis is 20~50m/min, mostly at 30m/min and 40m/min. The tool tip of the tool spindle is generally on or near the center of rotation of the B-axis to improve the machining quality of the workpiece surface and reduce the cutting force torque of the B-axis. Moreover, the U-axis is generally configured to increase the machining range, and the A-axis headstock can synchronize the double drive to increase the torque while reducing the torsional deformation of the blade machining.
Figure 1 Swiss Starr-Haycott five-axis linkage blade machining center
Figure 2 Swiss Ligit five-axis linkage blade machining center
Figure 3 Five-axis machining center of Ferrari, Italy
Figure 4 Hameler 5-axis linkage blade machining center in Germany
The domestic five-axis linkage blade machining center started late. The main types of machine tools for this type are Beijing Electromechanical Machinery Co., Ltd., Xinrui Machine Tool (Group) Co., Ltd., Sichuan Changzheng Machine Tool Group Co., Ltd. and Dalian Kede CNC Co., Ltd. The domestic five-axis linkage blade machining center has the XKH series of Beijing Electromechanical Machinery Co., Ltd., the LVC series five-axis linkage blade machining center of Sichuan Changzheng Machine Tool Group Co., Ltd., and the V5X1800 five-axis linkage blade processing of Jiangsu Xinrui Machine Tool (Group) Co., Ltd. Center and Dalian Cod Numerical Control Co., Ltd. KTurboM3000 five-axis blade milling machining center.
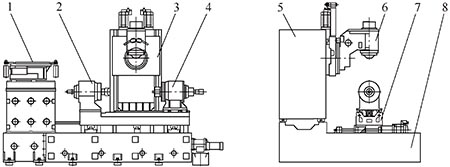
Beijing Electromechanical Machinery Co., Ltd. is the first manufacturer in China to successfully develop a five-axis linkage blade machining center. Its XKH series machine tool is based on the introduction of technology by Beijing Electromechanical Machinery Co., Ltd., applying foreign mature technology and combining the characteristics of blade parts. The professional blade processing machine designed and developed independently has a maximum processing blade length of up to 1 600mm. It has been successfully applied in batches in China. The users include Dongfang Steam Turbine Works, Wuxi Blade Factory, Dawn Engine Company and other OEMs, as well as supporting processing for the main engine factory. Professional blade processing plant. XKH series blade machining center adopts column moving structure, five-axis linkage, all coordinates full-closed control, the tool realizes X and Z axis motion through the column, slide plate and other components. The A-axis is directly driven by the torque motor, the response speed is fast, and there is no transmission gap. The workpiece can be rotated to achieve high-speed and high-precision machining of the blade. It can also be driven by a worm-gear structure. The B-axis adopts an optimized “heart-to-center†structure, and the axis deviates from the end surface of the tool spindle, but it is basically coincident with the tool tip. The pendulum torque is balanced by the spring balance device, and the torque motor and the worm gear are available. The workpiece A-axis tailstock can be moved along the U-axis according to the size of the different blades. The U-axis movement has two manual and servo motor drives. The form can be hydraulically locked to the tailstock after the workpiece is clamped to ensure the machining accuracy. It is suitable for steam turbines, gas turbines, aero-engine dynamic and static blades and various narrow and long special types made of high-strength steel, stainless steel, high-temperature alloy, titanium alloy and other difficult-to-machine materials. The processing of surface parts has been applied in batches in the fields of energy and aviation. Figure 5 shows the physical and structural diagram of the XKH800Z five-axis linkage blade machining center.
2. Automatic blade production line
With the introduction of "Industry 4.0" and "Made in China 2025" and the development of new technologies, the degree of automation of blade processing is also increasing. The degree of blade processing automation plays an important role in blade processing efficiency and processing quality.
Blade processing automation is based on the use of advanced technology, using modern mechanization and automation technology, using automatic devices and equipment to automatically operate the blade processing in the most efficient state to accelerate the production input state transformation and flow speed, so that processing Collecting, storing, exchanging, processing and transmitting information on the programming, production technical work, planning, scheduling, and operation management of the operation, so as to achieve the best goal of the integrated blade production, so that the production plant can be more successful. To meet the requirements of adapting to the needs of the society, and effectively increasing the income of the manufacturers.
(a) XKH800Z five-axis linkage blade machining center entity diagram
(b) XKH800Z five-axis linkage blade machining center structure
Figure 5 XKH800Z five-axis linkage blade machining center
1. Tool magazine 2. Head frame 3. B-axis box 4. Tail frame 5. Column 6. Headstock 7. Workbench 8. Bed
The significance and benefits of blade processing automation are enormous: 1 Improve equipment utilization. This is due to a reduction in processing time or auxiliary time. At present, the utilization efficiency of most independent blade processing machines in China is between 30% and 40%, and the utilization efficiency of some foreign machine tools using automated production lines can reach more than 70%. 2 reduce the cost of the product. This is due to the reduction in product scrap rate and equipment productivity, the reduction of intermediate reserves, the simplification of the transportation route and the reduction of employees, the reduction of plant area and the simplification of production scheduling. 3 improve product quality. This is because the effects of human factors are reduced and eliminated. 4 Reduced a large number of workers. This is due to the use of automated equipment to achieve multi-machine management, and even unmanned production. 5 fundamentally improve working conditions and reduce production damage. 6 Improve corporate image and enhance corporate competitiveness. In addition, automated production requires workers to master higher skills, which can narrow the gap between physical and mental work.
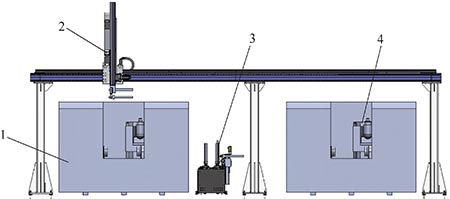
There are not many manufacturers of five-axis linkage blade machining centers that can realize automatic loading and unloading in foreign countries. At present, only Italy Ferrari and Germany HAMILL produce automatic loading and unloading production lines with workpieces. From the domestic perspective, only the Beijing Electromechanical Machinery Machine Tool Company has developed a five-axis linkage blade machining center production line (see Figure 6).
Figure 6 5-axis linkage blade machining center production line
1,4. Blade processing machine 2. Truss manipulator 3. Silo
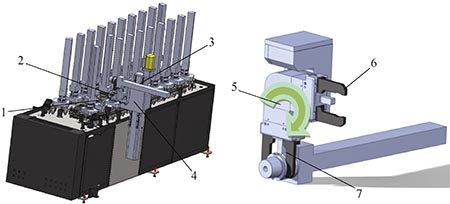
Placement method Each two machine tools form an automatic production line with a silo in the middle. The silo cycle drive adopts a chain form, and the drive form is driven by a servo motor. To save space, the workpiece is placed in the silo and the gripping posture is In the 90° form, a servo-driven hand grip and a swing cylinder are attached to the silo for the preparation of the mandrel. The silo form is shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7
1. Auxiliary hand grasping 2.5. Swinging cylinder 3. Loading posture 4. Auxiliary manipulator 6. Unloading hand grasping 7. Loading hand grasping
The loading and unloading process of the truss mechanical arm to the machine tool is as follows: the mechanical arm moves in the negative direction of the X axis (ie, to the left) to the top of the left machine, waiting for the machining to be completed. When the machine tool is finished, the automatic top door opens and sends a signal to call the robot arm for refueling. The Z-axis of the robot arm moves down to the programmed position (ie, the center position of the machine tool spindle), the grip is gripped, and the machine tool clamp is released. The robot arm moves in the positive direction of the X axis, so that the pallet is completely separated from the machine spindle. The mechanical arm swings the cylinder by 90°, so that the loading hand is grasped downward. Then, the robot arm moves in the negative direction of the X axis, so that the pallet enters the machine tool spindle, and then the machine tool clamp is clamped, and the robot arm is gripped and released. The Z axis moves up to the top of the machine, and the robot arm sends a signal to inform the machine that the loading and unloading is completed, and the top door of the machine is closed for processing. The pendulum of the robot arm swings 90°, so that the blanking hand is grasped downward. Then the robot arm moves in the positive direction of the X-axis to the upper side of the auxiliary robot, and continues the action of refueling with the auxiliary robot.
After the mechanical hand-feeding, the head and tail frame cooperate with the manipulator to realize the automatic clamping and positioning of the workpiece, which can realize one-time clamping and complete the processing of multiple spatial surfaces including the profile, the boss, the leaf crown and the leaf root rounding. In order to improve the machining precision of the blade and meet the requirements of the blade machining process, the servo force control of the tailstock movement can realize the adjustment of the clamping force of the workpiece during the rough and finishing process of the blade.
3. Conclusion
With the rapid development of the power, energy, aerospace and defense industries, the production capacity of steam turbines and aero-engines will be further expanded, and the demand for high-end five-axis linkage blade milling equipment will also increase significantly. It is an urgent requirement for the entire blade industry to develop a domestic five-axis linkage blade machining center with excellent quality, reduce the cost of blade processing machine tools, and meet the needs of the blade industry.
Blade machining automation solves the problem of mass and efficiency of mass production of blades, and has achieved good results in production.
references:
[1] Yan Kehui. Development Status and Structural Characteristics of Five-Axis Linkage Blade Machining Center[J]. Metal Processing(Cold Processing),2011(2):24-27.