Fossil fuel resources limited flammable ice has become the focus of human attention (Figure)
What about fossil fuels such as oil and natural gas? The flammable ice is considered as the best alternative energy source.

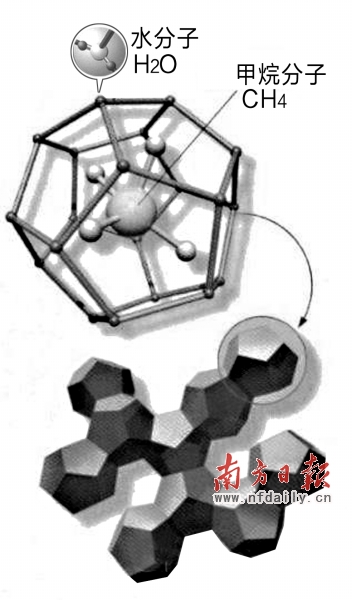
Combustible ice molecular structure diagram
According to related data, the total amount of global flammable ice is approximately twice as much as the proven total carbon content of traditional fossil fuels, which can be used by humans for thousands of years. The long-term resources of flammable ice in sea areas in China are only related to sea and land oil and gas resources. The amount is quite. By studying the development of flammable ice, many countries in the world may realize energy self-sufficiency, and the existing world energy trade may completely change.
Recently, at the National Symposium on "Marine Geology, Mineral Resources and Environment" held in Guangzhou, the results and prospects of flammable ice exploration have become one of the focuses of attention.
The author was informed that at present, China's special operations for the prospecting of flammable ice are organized and implemented by the China Geological Survey Bureau and undertaken by the Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey, mainly in the northern part of the South China Sea. Up to now, only in the seven prospects, 19 metallogenic belts and 25 metallogenic blocks circled in the northern part of the South China Sea, the prospective resources of flammable ice have reached 10 billion tons of oil equivalent.
At present, at least 40 countries have launched national-level resource surveys and research on flammable ice. If there is no oil in the future, humans may be able to ignite flammable ice and continue the dream of the energy of the century.
Century Energy
Usually 1 cubic meter of combustible ice can decompose more than 170 cubic meters of methane gas under normal temperature and pressure, which is praised as the 21st century green energy
Combustible ice, as the name implies, is the ice that can be burned.
Judging from the flammable ice produced in Russia, the United States, and Canada, most of them present ice-like crystals that are similar to the solid alcohols we use every day. However, from the first sample of natural gas hydrates drilled in the northern part of the South China Sea in the area of ​​the Shenhu area in 2007, it appears to be mud-like, with some delicate, dense, tiny white spots dispersed.
Professor Liang Jinqiang, deputy director of the Institute of Mineral Resources of the Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey, said that the combustible ice in the natural world is mainly found in high-latitude terrestrial frozen soil belts and marine continental slope sediments.
The formation of flammable ice requires three basic conditions: temperature, pressure, and raw materials. Take the seabed as an example. First, flammable ice can be generated above 0°C, but it will decompose when the temperature exceeds 20°C, and the seafloor temperature is generally maintained at 2-4°C. Secondly, when combustible ice is at 0°C, only 30 atmospheres are required. It can be generated, but with the depth of the ocean, 30 atmospheres can be easily ensured, and the greater the pressure, the less likely the hydrates will decompose. Finally, the rich carbon in the sediments of the ocean floor undergoes biotransformation and can generate sufficient air resources. The submarine strata are porous media. Under the conditions of temperature, pressure, and gas source, combustible ice will be generated in the interstitial spaces of the media.
According to the latest research results, the main distribution areas found in the world's bottom flammable ice in the world are the Gulf of Mexico in the Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea, the eastern continental margin of South America, the continental margin of West Africa, and the Black Sea Terrace outside the US East Coast. The Bering Sea, the Okhotsk Sea, the Thousand Islands Trench, the Okinawa Trough, the Japan Sea, the Shikoku Trough, the South China Sea Trough, the Sulawesi Sea, and the New Zealand North Seas in the sea area, the Central American Trough in the Eastern Pacific Ocean, California off-shore And the Peruvian trough, etc., the Gulf of Oman in the Indian Ocean, the Ross Sea and Weddell Sea in the Antarctic, the Barents Sea and Beaufort Sea in the Arctic, and the Black Sea and Caspian Sea in the mainland.
Combustible ice is a clean energy source with high energy density. According to Liang Jinqiang, usually 1 cubic meter of combustible ice can decompose more than 170 cubic meters of methane gas under normal temperature and pressure. It is the best alternative energy source for oil and natural gas and is praised as the 21st century green energy. The flammable ice composition is similar to the natural gas composition that people usually use, but it is purer. It can only release the massive methane gas by heating and decompressing solid flammable ice. Therefore, it is known as the most commercial in the 21st century. One of the strategic resources for development prospects.
According to foreign data, flammable ice is widely existed in the world. This point has been widely recognized by researchers. About 27% of land on Earth is a potential area that can form flammable ice, and about 90% of the world's oceanic waters are also such potential areas. It is estimated that the total amount of natural gas resources contained in the global flammable ice is approximately 2.1×1016 cubic meters, which is equivalent to twice the total amount of traditional fossil fuels in the world. The latest estimate is up to 1.2×1017 cubic meters for human use. millennium. By studying the development of flammable ice, many countries in the world may realize energy self-sufficiency, and the existing world energy trade may completely change.
China strategy
The flammable ice prospective resources in China's sea area can reach several hundred million tons of oil equivalent, and the resource potential is huge. At present, flammable ice has been included in the national "Twelfth Five-Year Plan" energy development plan.
The current oil shortage has become a bottleneck restricting the sustainable development of China's economy and society. In 2009, China’s crude oil imports were nearly 200 million tons, and the foreign dependence was over 50%. It is urgent to find new alternative energy sources.
Liang Jinqiang told the author that according to related research reports, there are abundant flammable ice resources in the sea areas and land areas under China's jurisdiction, and the flammable ice prospective resources in China's sea area can amount to several ten billion tons of oil equivalent, and the resource potential is huge. It is roughly related to China's sea areas and land oil and gas. The amount of resources is quite the same. Therefore, China is also bound to conduct in-depth research on flammable ice exploration to solve the problem of energy shortage.
China began to pay attention to this new resource from the 1980s. In 1999, under the organization of the China Geological Survey of the Ministry of Land and Resources, the Guangzhou Ocean Geological Survey carried out a preliminary investigation of the flammable ice resources in the Xisha Trough of the South China Sea for the first time, and discovered comprehensive seismic anomalies in the combustible ice layer. In 2002, a special project for the investigation and evaluation of flammable ice resources in the sea area of ​​China was formally initiated. The China Geological Survey Bureau is responsible for the organization and implementation of the project. Special investigations are undertaken by the Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey. This is China's first major ore-finding action against flammable ice and new energy.
According to the Guangzhou Ocean Geological Survey, China’s first acquisition of tangible samples of combustible ice in the northern part of the South China Sea in the area of ​​the Shenhu area in 2007 has become the fourth country in the world after the United States, Japan, and India to collect physical samples of hydrates through a national R&D plan. It indicates that the level of China's flammable ice investigation and research has entered the world's advanced ranks. It is understood that eight drilling stations have been successfully implemented in the area of ​​the Shenhu Sea, and natural gas hydrate samples have been obtained at three of the stations. High-methane gas hydrates have been discovered for the first time, which has the characteristics of large thickness and high saturation.
On September 25, 2009, China’s geological department discovered combustible ice on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. This is the first time China has discovered flammable ice on the land. After China became Canada and the United States, it discovered flammable ice on the land through national plan drilling. The third country.
At present, after nearly 10 years of exploration, a series of pioneering achievements have been made in the investigation of flammable ice resources in the sea area of ​​China. It not only divides favorable gas hydrate formation areas through the study of formation conditions, but also analyzes conditions of temperature, pressure, sedimentation, structure, and gas source formed by natural gas hydrates, and identifies geophysical, geological, and geochemical anomalies based on natural gas hydrates. , Carry out prospective areas, metallogenic belts, metallogenic blocks, and drilled favorable blocks.
The author learned from the national symposium on marine geology, mineral resources and environment held in Guangzhou last month that at present, China has circled seven prospects in the northern part of the South China Sea, 19 metallogenic belts and 25 metallogenic blocks. The long-term resources amounted to 10 billion tons of oil equivalent. Only 11 flammable ice ore bodies in the area of ​​the Fox drilling area have reached an area of ​​about 23 square kilometers, and the gas resources are about 19.4 billion cubic meters. It is reported that the current flammable ice has been included in the national "Twelfth Five-Year Plan" energy development plan, and will further increase investment in the future.
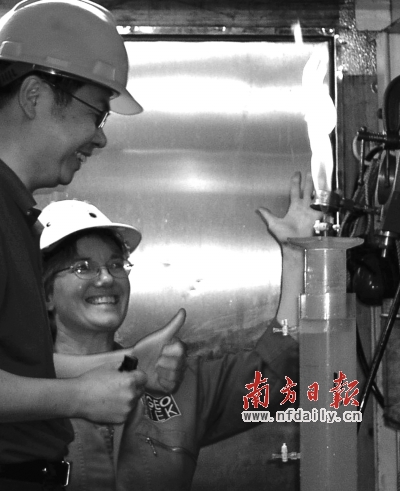

Photo source: Nanfang Daily
Application bottleneck
The exploitation of marine flammable ice is much more difficult than land on a technical level. Many developed countries are stepping up research, but there are no mature development technologies.
Liang Jinqiang introduced that the exploration and development of flammable ice is a systematic project involving many disciplines, such as marine geology, geophysics, geochemistry, fluid dynamics, thermodynamics, drilling engineering, geological experimental techniques, marine biology, etc., and vigorously developing flammable ice exploration. Development and research can promote technological advances in basic research such as marine geology, mineral resources, and global changes in various countries of the world, and can promote the development of related industries to form new economic growth points.
China's manned submersibles, the "Dragon", which has attracted wide attention this year, can be directly used to obtain "flammable ice" samples.
However, there are still many obstacles to the exploration, development and application of flammable ice. For example, methane in combustible ice has a greenhouse effect 20 times that of carbon dioxide, and the total amount of methane in seabed combustible ice around the world is about 3,000 times the amount of methane in the earth's atmosphere. If there is something wrong, let methane gas be in combustible ice. Escape into the atmosphere will have unimaginable consequences. In the process of flammable ice mining, it may also lead to softening of the seabed and geological disasters. For another example, the location of most of the deposits of combustible ice is likely to be too scattered, and it is also not conducive to economic exploitation.
Liang Jinqiang said that as a result, the scientific community has yet to reach a broad consensus on the exploration of flammable ice. Some people are skeptical about the huge resource potential of flammable ice, and others are concerned about the environmental damage caused by the development of flammable ice in the future. Just to implement it on the technical level, it also faces many problems. He explained that so far the only place where hydrate development has taken place is the Mesojaja gas field in the Siberian tundra. The United States and Canada have also successfully implemented trial mining in the terrestrial tundra, and onshore mining technology will gradually mature. In contrast, marine combustible ice mining is technically much more difficult than land. Many developed countries such as the United States, Japan, and South Korea are stepping up their research on marine combustible ice development technologies and have developed mining plans. However, at present, there are no Mature development of technical solutions.
For China, due to the reasons of intellectual property rights and technological protection in developed countries, domestic R&D progress has been slow. For instance, drilling sampling techniques, survey equipment, and test production development technologies have a wide gap with foreign countries.
However, Liang Jinqiang said that after the efforts of scientists, these problems are expected to be resolved in the near future. For example, at present, scientists have begun research on combustible ice and carbon dioxide replacement technology. Its purpose is not only to develop flammable ice resources more scientifically and rationally, but also to play an important role in reducing carbon dioxide and protecting the global environment. Once breakthroughs in mining technology have been made, combustible ice will immediately become the main energy source for the 21st century.
Glossary
The scientific name for combustible ice is called "natural gas hydrate." It is a combination of natural gas and water molecules under low temperature and high pressure conditions. Components that make up natural gas, such as CH4 (methane), C2H6 (ethane), C3H8 (propane), C4H10 (isobutane) equivalents, and CO2 (carbon dioxide), N2 (nitrogen), H2S (*hydrogen), etc. Single or multiple natural gas hydrates can be formed.
The main gas that forms natural gas hydrates is methane, and natural gas hydrates with a methane molecular content of more than 99% are often called methane hydrates. It can be represented by mCH4nH2O, where m represents the gas molecule in the hydrate and n is the number of water molecules.
Pure natural gas hydrates are white, resembling snow and ice, and can be directly ignited like solid alcohol. Therefore, they are vividly called “flammable iceâ€. Usually one cubic meter of combustible ice can decompose more than 170 cubic meters of methane gas under normal temperature and pressure, which is praised as the 21st century green energy.
The cross section of the "black chimney" is direct evidence of the presence of flammable ice.
On October 19, 2005, the Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey of the Ministry of Land and Resources announced a major breakthrough in the investigation of flammable ice in the South China Sea. The survey found a preliminary understanding of the extent and resources of combustible ice in the northern slopes of the South China Sea, and delineated a specific drilling target area. Xinhua News Agency
The gas released from combustible ice can burn in air.
On June 17, 2009, China's physical flammable gas sample “flammable ice†successfully obtained in the northern part of the South China Sea was unveiled in Guangzhou. China is the fourth country after the United States, Japan, and India to collect physical samples of natural gas hydrates through national-level R&D plans.
Full Power Emergency Battery Pack
The Full power emergency pack is ideal for LED tubes 3-40W Full power emergency output wattage for LED emergency lighting 60-180mins. Automatic lighting up when main power failures. Suitable for LED fitting with external led driver and internal driver. Widely using for parking lot, office, building, warehouse, school, hospital, workshop etc.
Emergency Lighting Battery Pack,Emergency Battery Pack For Led Lights,Emergency Power Packs,Bodine Battery Pack,led battery backup ballast
Foshan Nai An Lighting Electric Co.,ltd , https://www.emballast.com