When treating a neurological condition or restoring paralyzed limb function, it may be necessary to implant electrodes in the brain. But in the future, new hydrogels are expected to replace these electrodes to achieve better functionality. Conventional electrodes for nerve interfaces are usually made of rigid metals (such as gold or platinum). Because they do not match the softness of nerve tissue, they are usually coated with a flexible conductive polymer. Unfortunately, this will increase its area and make it appear more abrupt in the brain. In view of this, scientists from the Basque University of Spain, in collaboration with colleagues at the University of Strasbourg, France, have created an experimental new polymer hydrogel. Its body is based on starch, but it contains graphene which makes it highly conductive. Generally, in liquid materials such as hydrogels, the properties of graphene are not very stable. The good news is that adding substances extracted from sage can effectively overcome this problem. In addition, these extracts also have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. Of course, before graphene hydrogel replaces soft metal electrodes, scientists need further research and development. Ultra-Thin Ball Valve,Industrial Ultra-Thin Ball Valve,Thread Globe Valves,Threaded Swing Check Valve ZHITONG PIPE VALVE TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.ztpipevalve.com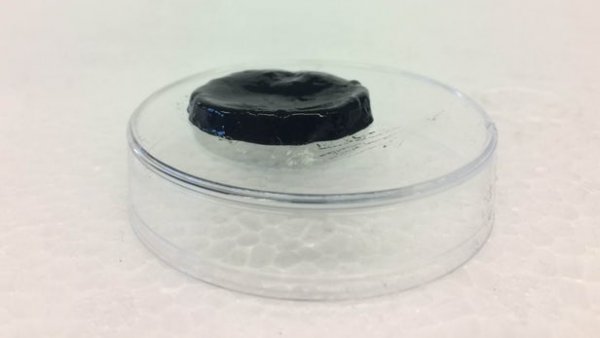
Conductive antibacterial hydrogel samples (Kizkitza Gonzalez / UPV / EHU) 
Research map