Pvc Double Doors,Interior Double Doors,Wood Entry Doors,Wooden Doors For Home Foshan QI'AN Fireproof Shutter Doors Co., Ltd , https://www.fsqianfiredoor.com
The main difference between the high lock nut and the ordinary nut is that the high lock nut can obtain the specified tightening torque and loose torque after installation, and is not easy to loose and fall off during use, and has high safety. Therefore, high lock nuts are widely used in aerospace products. The expected tightening torque and release torque of the high lock nut are obtained through the closing process. Therefore, the closing process is a process that must be performed for the high lock nut. The closing process is performed on a dedicated closing machine.
Figure 1 is the working panel of the closing machine. When the closing machine is working, the sliding cone sleeve slides perpendicularly to the surface of the table, thereby pushing the pressing head horizontally toward the center axis of the workpiece. When the pressing head is pressed to the outer circle of the part where the nut thread is located, The nut thread is deformed so that the nut thread forms an interference fit with the mating bolt thread to achieve the specified tightening torque and release torque. This process is called closing. The speed at which the indenter moves forward when the indenter presses the workpiece during the closing process is called the working speed, and the amount of deformation of the indenter pressing the workpiece is called the closing amount.
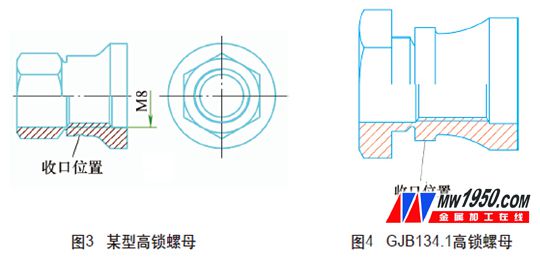
Figure 3 shows a high-lock nut developed by our company. The nut is similar in structure to the GJ B134.1 shear-type high-lock nut (see Figure 4). Since the nut is used in aerospace products, it is well known that the weight of parts of an aerospace product is as small as possible. Therefore, the outer diameter of the closing portion of the nut design is much smaller than that of the GJB134.1 high-locking nut, and it is because of such a difference that the manufacturing of the nut is greatly difficult, especially the closing process.
Microstructural continuity is one of the key indicators that the nut must be guaranteed. The design requires that the various parts of the nut should not have microscopic discontinuity defects such as cracking. Referring to the first batch of nuts processed by the GJB134.1 high-lock nut closing process, the metallographic inspection nut has a deep crack at the bottom of the thread, and the position is at the closing point. It is obvious that the crack is caused by the extrusion. After analysis, the main causes of cracks in the closing process are the following three aspects: The problem of the nut itself, the closing parameters are unreasonable, and the closing head is unreasonable.
The problem of the nut itself is mainly reflected in the wall thickness of the nut closing part is too thin, the thickness between the outer circle of the closing mouth and the large diameter of the thread is only 0.75mm. In addition, the material is made of super-hard aluminum, and the deformation is difficult, so the crack is easily generated by the closing extrusion. However, since the nut structure and material design have been fixed, it cannot be changed. Therefore, it is only possible to solve the crack problem from the closing process.
The closing parameters mainly include fast forward speed, work advance speed, dwell time, and closing amount. The main factors affecting the continuous are the speed of the work and the amount of closing. If the work speed is set too large, cracks are generated due to excessive deformation during extrusion. If the closing volume is too large and the extrusion deformation is too large, cracks may also occur. The closing amount is mainly determined according to the locking torque and the loose torque test data. Under the premise of ensuring the tightening torque and the loose torque, the smaller the closing amount, the less likely the crack is.
The first batch of cracked nuts, set the working speed of 300μm / s, from the locking torque and loose torque test data, the closing volume is also too large. Then we reduced the closing amount to the limit, and closed at 200μm/s, 100μm/s, 80μm/s, 60μm/s. After completion, the thread bottom still has different degrees of cracks, but cracks. The depth decreases as the work speed decreases. Immediately afterwards, we tested at a working speed of 20 μm/s. Due to the excessive extrusion time, the thread bottom formed many irregular tears. Through a large number of tests, a suitable workpiece speed of 60 ~ 80μm / s is obtained, but simply changing the working speed can not completely avoid the occurrence of cracks.
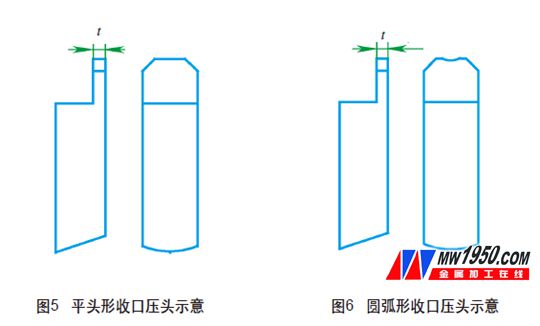
Before the closing, the flat head shape is used (see Figure 5). The thickness t determines the height of the embossing. When the thickness of the nip is too small, the nut receiving position is very large due to the small pressing force. Shear force.
In addition, due to the smaller deformation area of ​​the cuff, when the nut is screwed with the mating bolt, the friction area is small, so a large closing amount is required to achieve the specified locking torque and release torque, thereby affecting the continuity of the nut microstructure. . We adjust the thickness of the indenter from the initial P (P is the thread pitch) to 1.2P, 1.4P, 1.5P, 1.7P, 2P, 2.3P, 2.5P, and blunt the sharp edges of the indenter into rounded transitions. Carry out the closing test.
According to the metallographic examination, the crack depth gradually becomes shallower with the increase of the thickness of the indenter, but the locking torque becomes unstable after the closing width exceeds 2.3P. According to the test, the thickness of the indenter is 1.7P≤t≤2P. However, cracks are still not completely avoided.
Through careful analysis, we finally designed the circular arc-shaped closing head of Figure 6. Compared with the flat-headed crimping head, the arc-shaped crimping head has the advantage that the contact area of ​​the circular-shaped indenter and the nut increases, and the force is applied. The area is increased accordingly, so that the closing amount is much smaller than the flat head to achieve the specified locking torque and loosening moment, and the force is uniformly dispersed by the concentration. After the round-shaped crimping head was used to close the mouth, no defects such as cracks were found by the company's testing center and the third-party testing center. The closing research was successful.
About the author: Wang Liqiang, engineer, Zhejiang High-end Fastener Co., Ltd.